
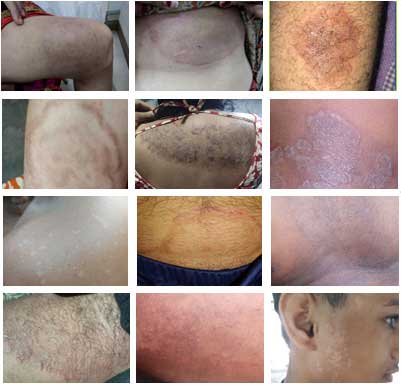
Fungal infection(mycosis) is a very common disease. Fungus can affect any part of the body but increasingly doctors at Kayakalp Global have found a higher incidence of fungal infection on the skin.
Fungi usually live in warm and moist areas where skin surfaces meet such as genital areas, toes, under the breast. They mostly live on the topmost layer of skin and rarely penetrate deeper.
Obese people with poor hygiene often encounters this disease due to excessive skin folds that is good habitat for fungus.